What is Bitcoin Mining Centralization and Why is it a Concern?

When he built Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto envisioned a decentralized digital currency that could function without the need for centralized institutions like banks and governments.
Satoshi did not envision a situation where a few entities controlled a significant portion of the entire network, essentially centralizing power and influence.
Bitcoin mining centralization, a result of market competition over the years, goes against the fundamental principle of cryptocurrency.
What is Bitcoin Mining Centralization?
Bitcoin mining centralization is the concentration of mining power among a few dominant players. Originally, anyone with a computer and internet connection could mine Bitcoin. However, the network grew with time and as a result mining became more competitive.
This led to the development of specialized chips known as ASICs (Application Specific Integrated Circuits), which outperformed GPUs and CPUs by being more efficient. Unfortunately, ASICs are expensive and out of reach for most people, and the fact that newer, better, but more expensive versions are being released makes the situation worse.
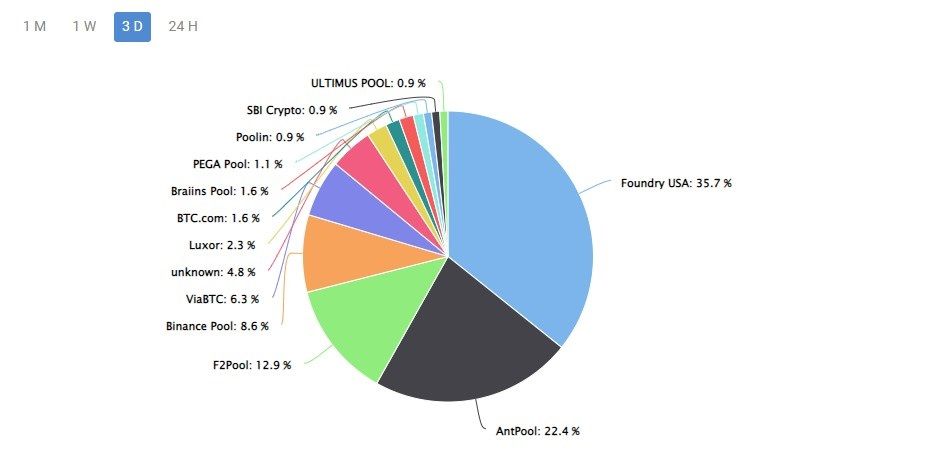
Miners started forming pools to combine their computing power and share the rewards they received. The biggest pools are also acquiring the latest technology to stay ahead of the competition, causing others who couldn’t keep up to drop out.
Over time, a few large mining pools, including Foundry USA, Antpool, and F2Pool, have come to dominate the Bitcoin mining industry, controlling a significant percentage of the total hash rate at any given time. This defeats the logic of cryptocurrency, which is meant to distribute power among many players.
3 Reasons for Bitcoin Mining Centralization
Several factors contribute to the centralization of Bitcoin mining. Most of these factors also apply in a typical competitive market. They include
- Economies of scale: As mentioned earlier, Bitcoin mining is very competitive. Miners who solve complex hashes and verify the most blocks remain profitable. And to do that they need expensive specialized hardware like ASICs. So they come together and form large mining operations to reduce costs and increase profitability.
- Entry barriers: Starting a Bitcoin mining company is very expensive. You need significant capital upfront for hardware. Still, it’s not as big a problem as maintaining it, since it uses a huge amount of power and can take years to make money. With this in mind, it is no wonder that potential investors will choose to join established mining pools over smaller ones.
- Legislation: In some jurisdictions, mining is subject to strict regulations, making it difficult for people to participate. For example, when China banned Bitcoin mining, trading and transactions, all mining moved to other countries, more to North America, which now accounts for almost 45% of the global hash rate.
- Power costs: Bitcoin mining is a power-intensive operation, and the more power a mining operation has, the better chance it has of staying competitive. So crypto miners set up shop in areas where electricity is cheap. As such, you will find mining pools forming in areas with cheap power supplies, leading to centralization.
3 Effects of Bitcoin Mining Centralization
While the centralization of Bitcoin mining is a natural process inspired by competition, it presents some challenges to the network and ecosystem.
- Reduced decentralization: The most notable effect of mining centralization is that it goes against the very reason it was built: to decentralize finance. Instead, a few entities gain significant control over mining, which is akin to governments printing money. This leads to security and integrity concerns in the event that the institutions are compromised.
- Risk of 51% attack: A 51% attack is an attack in which a group of miners who control over 50% of the mining hashrate perform selfish actions. As mining becomes more centralized, the risk of such an attack increases. A good example is Bitcoin Gold’s 2020 51% attack, which saw $70,000 worth of BTG spent twice.
- Control over the blockchain protocol: As well as the increased risk of launching a 51 percent attack, the united entities with significant control over the mining power can dictate the development of the Bitcoin protocol and potentially change it in favor of their interests. However, if such a change is detected earlier by the wider Bitcoin community, it can be rejected.
All of these challenges require careful consideration and action if the integrity and security of the Bitcoin ecosystem is to be preserved. But how?
How can crypto mining be decentralized?
Over time, various parties have proposed ways to solve the centralization issue.
Bitcoin Core developer Matt Corrallo proposed the BetterHash protocol, which involves decentralizing the selection of transactions that go into a block to individual hardware operators. However, it did not provide a mechanism that would ensure that miners will choose transactions that create a balanced difficulty for the Bitcoin network and thus open a new loophole for centralization. It also introduced inefficiencies due to the need to constantly monitor the network, which was difficult to deploy.
Meanwhile, crypto mining pool P2Pool proposed decentralizing payouts to solve the problem. However, by decentralizing payouts, small miners who rely on consistent payouts to cover their costs will be disadvantaged. It also required low-latency connections between miners and the P2Pool server, which meant that every time a miner experienced high latency, their mining performance would be negatively affected. For these reasons, it did not encourage adoption.
The most direct way to solve Bitcoin mining centralization is to decentralize the mining pools. This can be achieved through incentives that encourage the use of smaller and more decentralized mining pools. A practical incentive would be to fund innovation and experimentation by small miners, leading to better and more competitive mining strategies.
In particular, former Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey’s payments company, Block, began working on an open Bitcoin mining system to make the network more decentralized and permissionless. Block aimed to build its own high-performance open source ASIC and a Bitcoin wallet to make Bitcoin custody more mainstream.
Yet incentives alone may not be enough to encourage decentralization. Regulatory policies, network upgrades, and community initiatives may also be necessary to encourage the growth of smaller and more decentralized mining pools.
Will Bitcoin Mining Be Decentralized?
It is difficult to predict that Bitcoin mining will become more decentralized. Mining power will remain centralized among dominant players as mining becomes more expensive.
Due to economies of scale and other bottlenecks, smaller miners continue to battle the big dogs. As a result, it will require enormous efforts from the rest of the Bitcoin network to implement strategies and solutions to solve Bitcoin mining centralization.