What is a Blockchain Ecosystem?

A blockchain ecosystem refers to the different parts that make up a blockchain network and how they interact. Everyone serves a role in the blockchain and is part of how it works.
Although blockchain networks have similarities, each one is unique. The elements of blockchain ecosystems can vary. For example, Bitcoin (CRYPTO:BTC) and Ethereum (CRYPTO:ETH) has two very different blockchain ecosystems, with Ethereum having a much wider range of projects and services.
Blockchain ecosystems are an important topic for crypto investors. The ecosystem shows how a blockchain works, and it can often help us figure out the current state of health of a blockchain. In this guide, you will learn more about blockchain ecosystems and see some of the most notable examples.
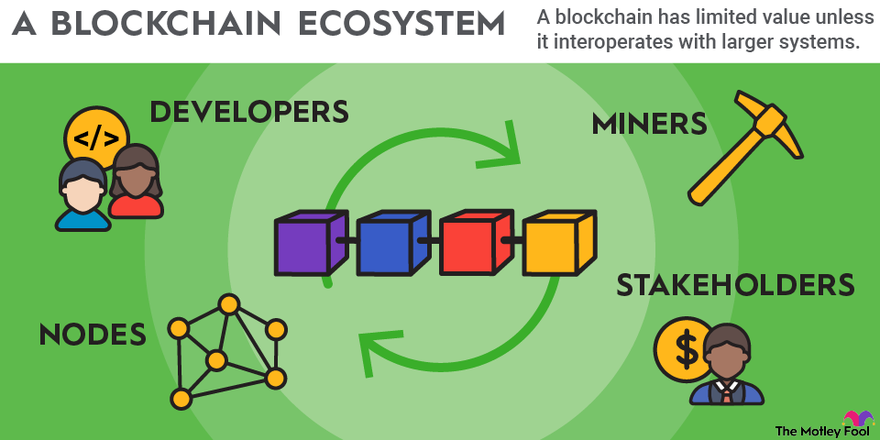
Image source: The Motley Fool
How a blockchain ecosystem works
At its most basic level, a blockchain is a type of distributed ledger, or database. It is distributed across different blockchain nodes and it is completely decentralized, meaning that there is no single entity that controls it. The data is stored in blocks that connect to each other, hence the name.
The elements that make up and contribute to the blockchain are its ecosystem. Elements you will find in any blockchain ecosystem are:
- Developers: The parties that build and update the blockchain network.
- Nodes: Devices that run the blockchain’s software and keep an up-to-date history of the transactions.
- Miners/Validators: Participants in the blockchain’s transaction validation process. A blockchain can have either miners or validators, depending on the validation system it uses.
- Stakeholders: Holders of the blockchain’s original cryptocurrency. This includes people who have bought it as an investment in cryptocurrency and who plan to use it for payments. With some blockchains, stakeholders have the right to create and vote on proposals, giving them a say in the future.
While these are the core elements of a blockchain ecosystem, they are often just the beginning. Starting with Ethereum, many modern blockchains have launched with the ability to run smart contracts. A smart contract is a self-executing blockchain contract, like a program that runs on a blockchain.
Smart contracts dramatically expand the capabilities of blockchain technology, and they introduce a new group into a blockchain ecosystem—the projects built on that blockchain. Here are just some of the types of projects that can be created on a smart contract blockchain:
When someone refers to the Ethereum ecosystem or Cardano (CRYPTO:ADA) ecosystem, to use two popular examples, they usually talk about the projects on the blockchain network. The projects can be a solid way to measure how well a blockchain is doing and its potential as an investment.
If a blockchain has a large ecosystem with a diverse range of projects, that’s a good sign. This is one reason why Ethereum is such a popular investment.
The reverse is not always true. Blockchains that are still in the development stage can be valuable investments even if they don’t have much of an ecosystem yet. But at some point it is important for a blockchain to move beyond the theoretical and actually attract users.
Did you know…
A blockchain has limited value unless it works together with larger systems.
Blockchain Ecosystem List
The cryptocurrency market is full of blockchain ecosystems. Let’s take a look at some of the biggest and most important.
Bitcoin
Bitcoin is the cryptocurrency that started it all and the largest by market capitalization. However, the Bitcoin ecosystem is more limited compared to many of the blockchains that have emerged in the years since its launch.
The purpose of Bitcoin, as described in the Bitcoin White Paper, is to be a peer-to-peer electronic payment system. It still does, although it is now often used as a store of value. Since it is designed as a digital currency, Bitcoin’s ecosystem relies on a large number of nodes and miners using its proof-of-work system to record transactions.
It also has an active development community, with developers primarily working on fixing bugs and making functionality improvements.
Ethereum
There is arguably no blockchain ecosystem more impressive than Ethereum. It was the first smart contract blockchain platform, a key competitive advantage that enabled it to build a strong developer community. It is also known for being developer friendly. In particular, the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) helps simplify the process of launching decentralized apps (dApps).
As a result, the Ethereum ecosystem is home to some very popular projects. Examples include:
Binance
Binance is different from the other blockchain ecosystems we’ve looked at because it’s not just a blockchain. It is primarily a cryptocurrency exchange with its own native cryptocurrency, GDP (CRYPTO:BNB). Binance also has a smart contract blockchain, BNB Chain (originally called Binance Smart Chain).
With its smart contract capabilities, the BNB chain is one of many competitors to Ethereum. The wider Binance ecosystem is also home to a blockchain project lab, a crypto token launch platform, a digital crypto wallet called Trust Wallet, and much more.
Stellar
Stellar (CRYPTO:XLM) is built around the original purpose of cryptocurrency – to be a decentralized payment network. It is highly efficient as transactions are processed in seconds and cost a fraction of a cent. Stellar is also compatible with all types of fiat money.
The Stellar ecosystem is home to several businesses and projects looking for payment solutions. IBM (NYSE:IBM) built its global payment system World Wire, which facilitates international payments with digital currencies, on Stellar. MoneyGram International (NASDAQ:MGI) is also part of the Stellar ecosystem. It has a crypto-to-cash service powered by the Stellar blockchain.
As you can see from just a couple of examples, there are many different types of blockchain ecosystems. If you’re thinking about investing in a blockchain project, the ecosystem is a good place to start your research.
Lyle Daly has positions in Binance Coin, Bitcoin, Cardano and Ethereum. The Motley Fool has positions in and recommends Aave, Bitcoin and Ethereum. The Motley Fool recommends the Uniswap Protocol Token. The Motley Fool has a disclosure policy.