Here’s what to expect from the groundbreaking move

The mythical merger is finally coming to fruition. And after a rough year for the crypto world, Ethereum’s long-awaited software update could inject some much-needed energy into the Web3 space while scoring a significant win for the environment.
The transition, many years in the making, is technically sophisticated, controversial and likely to be the biggest event in the crypto space for some time to come. So let’s break down what the merger is, why it’s important, and what it means for the future of the crypto and NFT space.
What exactly is the merger?
The Ethereum blockchain is the technical infrastructure that allows countless Web3 applications and crypto and NFT projects to exist. At its most basic level, the merger (sometimes called Ethereum 2.0, Eth 2, or ETH 2.0) is an upgrade to the Ethereum blockchain that will reduce environmental impact, increase network security, and enable Ethereum developers to introduce new features and increase scalability to the chain.
So, what is merging, exactly? The update will combine Ethereum’s main network (blockchain) with the Beacon Chain, a separate blockchain created in 2020 that has since run parallel to Ethereum.
The Ethereum network is what developers call the execution layer of the blockchain network. Execution layer creates a place for applications to live and process transactions that are related to those applications. You can think of this as the construction that allows data transfers on the blockchain to take place. Execution layers give you the power to execute a transaction.
The Beacon Chain is the consensus layer of the system. The secret is in the name – this layer deals with enforcing network rules, validating (or invalidating) transactions that the execution layer “wants” to happen. Because blockchains are essentially decentralized public ledgers, they need a way to verify or invalidate the transactions that take place in them.
To do this and at the same time ensure that no one forges a transaction on the public ledger and steals cryptocurrencies or NFTs that do not belong to them, most computers in the system must agree on the validity of the transaction (block). This is how a blockchain governs itself without third parties.
Right now, the Ethereum mainnet uses a system called Proof of Work to validate transactions. Merging with Beach Chain will allow Ethereum to end the PoW consensus system in favor of another system called Proof of Stake. And that’s a big deal.
What is proof of work?
Proof of Work is one of the main reasons why blockchain technology has a less than stellar environmental reputation. Combined, the Bitcoin and Ethereum blockchains consume more than 317 TWh hours of energy annually, placing them right between Italy and the UK in terms of electrical energy consumption.
This huge energy consumption comes from the PoW consensus mechanism which involves complicated and energy-intensive computation, a process known as “mining”. To perform this mining, nodes in the network – which often take the form of giant servers that can span entire warehouses – solve complex mathematical problems based on cryptographic algorithms.
The process is energy-intensive by design. Requiring resource-intensive computing processes to try to mess with the ledger prevents people from doing so.
And how is proof of stake different?
Proof-of-stake consensus, which Beacon Chain will bring to Ethereum, is orders of magnitude less energy-intensive than PoW – 99.95 percent less intensive. That’s because PoS doesn’t require nodes in the network to solve complex calculations. Instead, it ensures network security by allowing users to stake an amount of their cryptocurrency in the hope that the system will randomly select them as a block validator.
Why the merger is important
Along with Bitcoin, Ethereum is one of the most popular blockchains in the world, with a market capitalization of nearly $190 billion at the time of writing. Aside from the millions of NFTs the blockchain authenticates, countless other decentralized apps and decentralized financial systems depend on the blockchain to function.
The blockchain also symbolizes the crypto and NFT movement and Web3 in general. A successful merger could be a much-needed shot in the arm to an ecosystem weathering another crypto winter. But while many see the merger as a big win for Ethereum and its environmental impact, not everyone is happy about it. The switch will directly affect the countless ETH miners worldwide who earn cryptocurrency to perform PoW calculations. The merger will essentially eliminate the need for their existence (along with the bottom line).
There is also some ideological controversy surrounding the merger’s effects on the decentralized nature of Ethereum. Several well-known Web3 entities – including Lido, Coinbase, Kraken and Binance – control large percentages of ETH on the Beacon Chain, leading some to fear that they could become targets of censorship attempts by government agencies.
Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin has indicated that he would support measures to burn the fire of any validators censoring Ethereum’s protocol at the behest of regulatory bodies, but the concern remains.
Another problem is what is known as the 51 percent attack scenario, a hypothetical situation where malicious actors collaborate to take over more than half of the validators in the network to falsify the blockchain record and steal crypto or NFTs. Doing this would be incredibly difficult, as a hacker would need to own the majority of ETH in the system to do so, which would be prohibitively expensive to acquire.
How will the merger affect gas taxes?
In a nutshell, it won’t.
Gas fees are the cost of completing a transaction on Ethereum, and they can skyrocket during busy periods (such as when an NFT project is minted), potentially adding hundreds of dollars to transaction costs. Unsurprisingly, Ethereum users are not too happy about this. However, the merger does not affect network capacity, so users will not see a change in this dynamic after the merger is complete.
The technical miracle behind the merger
In April, Cooper Kunz, CTO of Calaxy, a Web3 social marketplace, described the merger as “one of the most difficult, novel and impressive feats of engineering I think the world has ever seen,” in an interview with nft now.
He does not exaggerate. Ethereum developers have been working hard on the merger for years, delaying it several times in the process. In order to get a switch of this magnitude up and running, engineers have been conducting general tests for the merger over the past few months involving several Ethereum test networks (testnets) to check for errors or hiccups in the transition process. The last of these tests, which took place on the Goerli testnet, merged earlier this month.
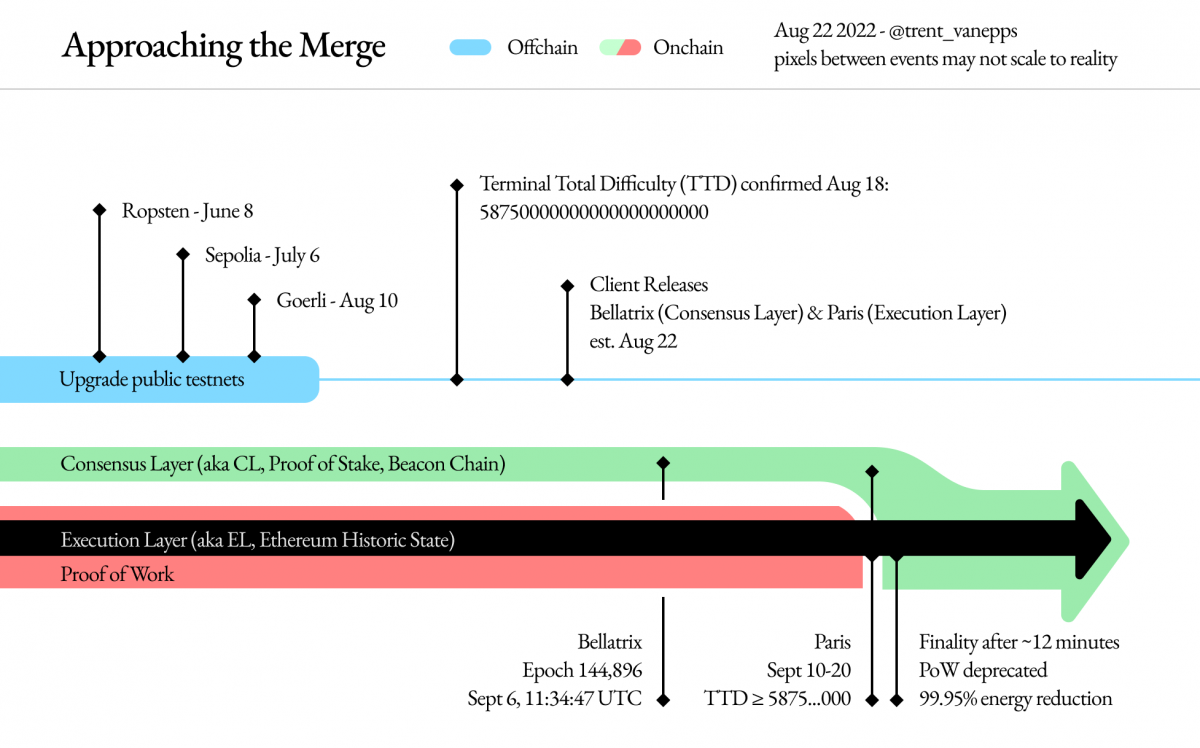
Two significant upgrades must also take place before the merger takes place. First is the Bellatrix upgrade, which enables merging on the Beacon Chain, followed by the Paris upgrade, which removes any reliance on proof-of-work mining.
When is the merger?
If all goes well, Ethereum developers expects the merger to take place during the week of September 15, 2022. However, there’s no guarantee, and given how long it’s taken for the merge to come this far, it wouldn’t be a huge surprise if the Ethereum team delayed it even further.
Still, it’s an exciting time to be in the crypto and NFT space. With any luck, the merger will go off without a hitch, and the Web3 community will have all the more reason to celebrate and promote a positive environmental message within and beyond its ranks.

























